Alpha Doradus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Alpha Doradus, Latinized from α Doradus, is the brightest 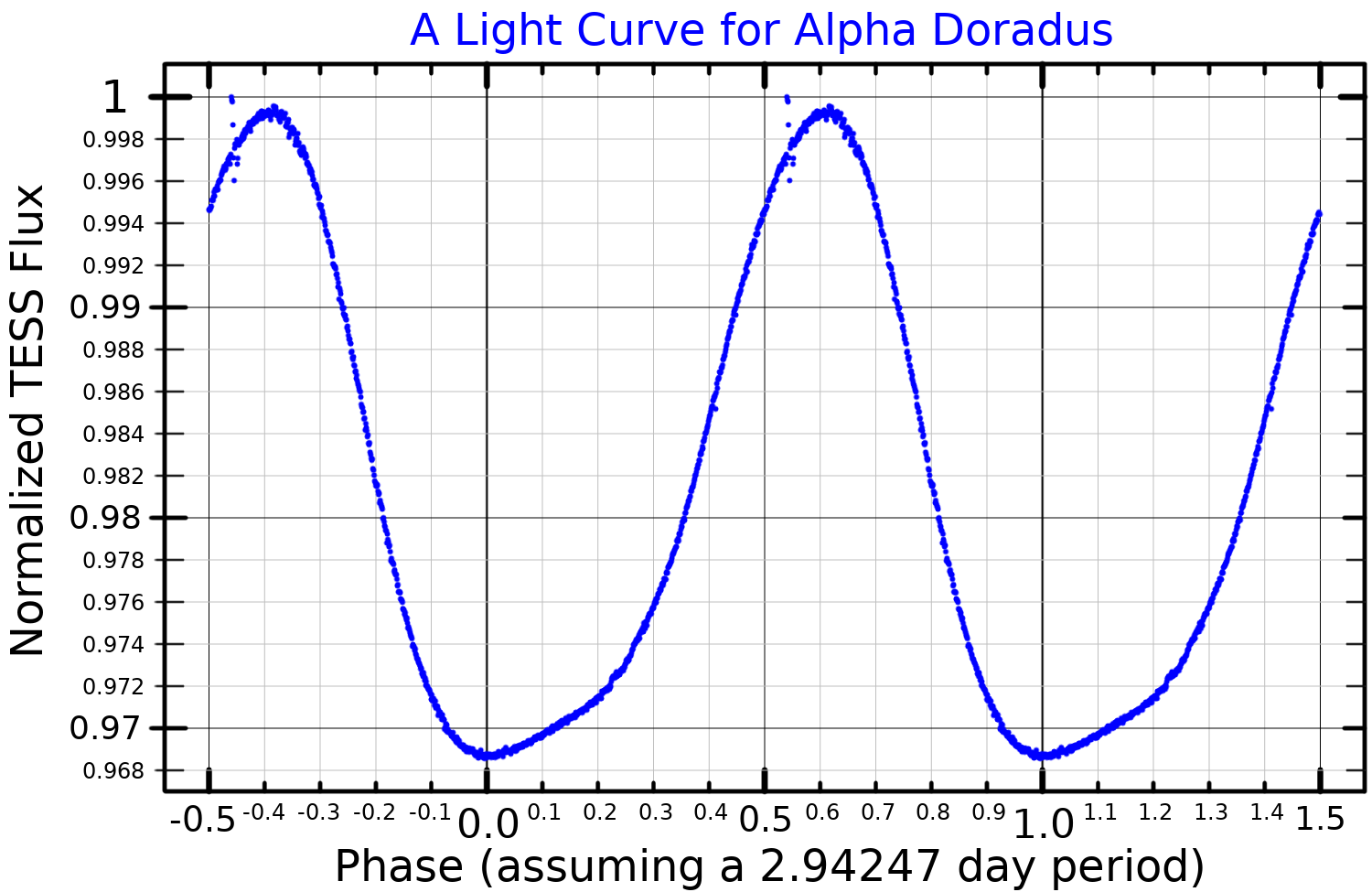 This is a
This is a
star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
in the southern constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
of Dorado
Dorado () is a constellation in the southern sky. It was named in the late 16th century and is now one of the 88 modern constellations. Its name refers to the dolphinfish (''Coryphaena hippurus''), which is known as ''dorado'' in Spanish, altho ...
. The distance to this system, as measured using the parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby objects ...
method, is about .
 This is a
This is a binary star
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in wh ...
system with an overall apparent visual magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's lig ...
that varies between 3.26 and 3.30, making this one of the brightest binary stars. The system consists of a subgiant
A subgiant is a star that is brighter than a normal main-sequence star of the same spectral class, but not as bright as giant stars. The term subgiant is applied both to a particular spectral luminosity class and to a stage in the evolution of ...
star of spectral type
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction grati ...
B revolving around a giant star
A giant star is a star with substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main sequence, main-sequence (or ''dwarf'') star of the same effective temperature, surface temperature.Giant star, entry in ''Astronomy Encyclopedia'', ed. Patrick Moo ...
with spectral type A in an eccentric orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a p ...
with a period of about 12 years. The orbital separation varies from 2 astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbits t ...
s at periastron
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion.
General description
There are two apsides in any elli ...
to 17.5 astronomical units at apastron
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion.
General description
There are two apsides in any el ...
. The primary, α Doradus A, is a chemically peculiar star
In astrophysics, chemically peculiar stars (CP stars) are stars with distinctly unusual Metallicity, metal abundances, at least in their surface layers.
Classification
Chemically peculiar stars are common among hot main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) ...
whose atmosphere displays an abnormally high abundance of silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
, making this an Si star.
Alpha Doradus has an optical companion
In observational astronomy, a double star or visual double is a pair of stars that appear close to each other as viewed from Earth, especially with the aid of optical telescopes.
This occurs because the pair either forms a binary star (i.e. a ...
, CCDM J04340-5503C, located 77 arcsecond
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The na ...
s away along a position angle
In astronomy, position angle (usually abbreviated PA) is the convention for measuring angles on the sky. The International Astronomical Union defines it as the angle measured relative to the north celestial pole (NCP), turning positive into the d ...
of 94°. It has no physical relation to the other two stars.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Alpha Doradus A-type giants B-type subgiants Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variables Binary stars Dorado (constellation) Doradus, Alpha CD-55 00916 029305 021281 1465